Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry (Ex – 12.3)
Question 1.
Find the coordinates of the point which divides the line segment joining the points (-2, 3, 5) and (1, -4, 6) in the ratio
(i) 2 : 3 internally,
(ii) 2 : 3 externally
Solution:
(i) Let P(x, y, z) be any point which divides the line segment joining the points A(-2, 3, 5) and B(1, -4, 6) in the ratio 2 : 3 internally.


(ii) Let P(x, y, z) be any point which divides the line segment joining the points 71 (-2, 3, 5) and B(1, -4, 6) in the ratio 2 : 3 externally. Then

Question 2.
Given that P(3, 2, -4), Q(5, 4, -6) and R(9, 8, -10) are collinear. Find the ratio in which Q divides PR.
Solution:
Let Q(5, 4, -6) divides the line segment joining the points P(3, 2, -4) and R(9, 8, -10) in the ratio k : 1 internally.

Question 3.
Find the ratio in which the YZ-plane divides the line segment formed by joining the points (-2, 4, 7) and (3, -5, 8).
Solution:
Let the line segment joining the points A(-2, 4, 7) and B(3, -5, 8) be divided by the YZ -plane at a point C in the ratio k : 1.


Question 4.
Using section formula, show that the points A(2, -3, 4), B(-1, 2, 1) and C(0,1/3,2) are collinear.
Solution:
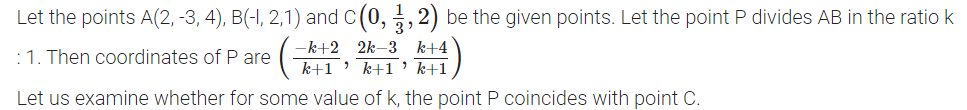

AB internally in the ratio 2:1. Hence A, B, C are collinear.
Question 5.
Find the coordinates of the points which trisect the line segment joining the points P(4, 2, -6) and Q(10, -16, 6).
Solution:
Let R and S be two points which trisect the line segment PQ.

